Unveiling Measles: Symptoms and Stages of a Highly Infectious Disease
Early hidden measles symptoms to look out for - plus 'four phases' of highly-infectious disease
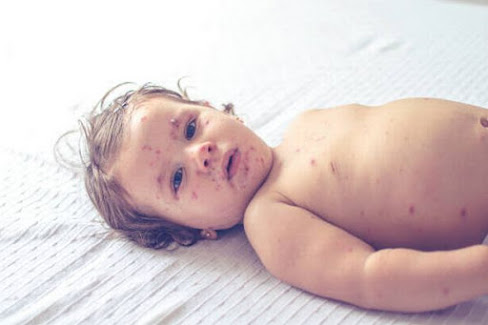
Councils are encouraging people to get their measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine, as measles makes a comeback(Image: North East Lincolnshire Council)
Introduction to Measles:
• Measles, or rubeola, is a viral disease causing deaths in young children globally despite vaccines.
• It's highly contagious and understanding its symptoms and stages is crucial.
• The measles rash is the characteristic sign, but there are distinct stages before it appears.
Incubation Period: Silence Before the Storm:
• For 10-12 days after exposure, the virus multiplies without symptoms.
• During this period, there's no visible sign of infection.
• This is the quiet phase where the virus sets the stage for the upcoming symptoms.
Prodromal Phase: The Onset of Symptoms:
• After incubation, initial symptoms like fever, cough, and runny nose emerge.
• Koplik's spots, a sign appearing inside the mouth, are often a key diagnostic indicator.
• This phase mimics severe cold or flu, making it hard to distinguish initially.
Acute Phase: Appearance of the Rash:
• The rash, typically red or reddish-brown spots, appears 3-5 days after initial symptoms.
• Starting behind ears and along the hairline, it spreads to face, neck, trunk, arms, and legs.
• The rash marks the peak of fever and can lead to severe complications if not managed well.
Recovery Phase: Gradual Convalescence:
• As the rash fades, fever and other symptoms also subside.
• Recovery begins, but it can be slow and may lead to fatigue.
• This phase is critical as complications can still arise, especially in vulnerable individuals.
Complications and Severity:
• Measles can lead to serious complications like pneumonia or encephalitis.
• Adults, malnourished children, and those with compromised immune systems are at higher risk.
• Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) is a rare but fatal complication of measles.
Prevention and Control: Vaccination
• Vaccination, especially the MMR vaccine, is highly effective.
• High vaccination coverage is crucial for herd immunity and preventing outbreaks.
• Community efforts to sustain vaccination are vital for the control of measles.
Conclusion: Managing Measles and Its Risks
• Early recognition and management of measles are essential to prevent complications.
• Seeking medical care is critical, especially for vulnerable groups.
• By focusing on vaccination and prompt treatment, measles can be effectively controlled, saving lives and preventing outbreaks.
Disclaimer:
This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
The original news article can be found [Here]


Comments
Post a Comment